
March 14, 2025
Supply Chain Finance in India: A Complete Guide
Supply Chain Finance is transforming how businesses manage cash flow and optimize working capital by connecting buyers, suppliers, and financial institutions. This financing solution is particularly vital for India’s Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), which account for over 95% of the country’s industrial units but often struggle to access affordable credit. Supply chain finance helps bridge this gap, offering a more flexible approach to liquidity.
In recent years, supply chain finance in India has seen significant growth. The India trade finance market, which includes these solutions, is projected to grow from $2.06 billion in 2024 to $3.18 billion by 2030, at 7.56% CAGR. In just five years, the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS), a platform that provides supply chain finance for MSMEs, saw invoice financing surge by 766% from FY20 to FY24, rising from 4.8 lakh invoices financed in FY20. This blog offers a complete guide to supply chain finance in India, exploring key products, operational mechanisms, real-world applications and the numerous benefits it offers.
What Is Supply Chain Finance
Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow by providing suppliers early invoice payments and buyers extended payment terms. It leverages technology to streamline transactions and includes financial institutions to provide the necessary funding.
It helps businesses unlock working capital by offering a cost-effective financing mechanism that enhances cash flow management.
Supply Chain Finance in India – Key Benefits for Different Stakeholders
Supply Chain Finance offers distinct advantages to various stakeholders involved in the lending process, creating a win-win situation for all parties.
Benefits for Buyers (Large Corporates)
- Extended Payment Terms: Through supply chain finance, large corporates can negotiate longer payment cycles to optimize their cash flow while ensuring timely supplier payments. This flexibility enables them to better allocate resources and manage their working capital without disrupting supplier relationships.
- Improved Supplier Relationships: Early payment options through this route help strengthen supplier relationships, leading to improved pricing, service and loyalty. This is especially crucial in industries where supply chain stability is vital.
- Better Financial Planning: Supply chain finance allows predictable cashflow management enabling businesses to budget more effectively and focus on growth initiatives, rather than being sidetracked with managing payment cycles.
- Reduced Financial Risk: Timely payments from supply chain finance reduces supply chain disruptions and mitigates default risks from suppliers.
Benefits for Suppliers (MSMEs)
- Improved Liquidity and Cash Flow: Supply chain finance allows MSMEs with better liquidity. Rather than waiting for long payment cycles, suppliers can receive immediate invoice payments. This allows them to reinvest in their business or cover operational costs without relying on traditional, expensive financing options.
- Lower Dependency on Expensive Loans: Instead of high-interest loans, MSMEs can use supply chain finance for quick invoice payments, avoiding costly debt because financing is based on buyer creditworthiness.
- Improved Business Relationships: Receiving prompt payment helps suppliers build a solid relationship with their buyers. It enhances trust and ensures they can continue meeting buyer demands on time.
- Access to Larger Markets: By improving cash flow, supply chain finance enables MSMEs to compete better by securing raw materials and fulfilling large orders, allowing them to expand capacity and access larger buyers they couldn’t otherwise service due to financial limitations.
Benefits for Financial Institutions (Banks and NBFCs)
- Lower Risk and Secure Transactions: Financial institutions benefit from reduced risk, as transactions are backed by buyers’ creditworthiness, typically large corporates with strong financial profiles, lowering default likelihood compared to traditional lending. This makes supply chain finance a safer, portfolio diversifying investment option.
- New Revenue Streams: Financial institutions gain a new revenue stream through supply chain finance, generating income from transaction fees and providing suppliers with quick working capital.
- Broader Larger Client Base: Supply chain finance enables financial institutions to build relationships with both suppliers (MSMEs) and buyers (large corporates). This helps in expanding their client base, deepening market penetration and creating opportunities to offer customized financial products to both.
- Operational Efficiency and Transparency: Technology-enabled supply chain finance automates processes like invoicing, payment tracking and financing, which reduces administrative costs and improves the efficiency of financial lending operations.
- Promotes Financial Inclusion: It promotes financial inclusion by providing MSMEs affordable financing, enabling financial institutions to access underserved markets and serve businesses typically excluded from traditional lending due to lack of collateral or credit history.
Types of Supply Chain Finance in India
Supply chain finance in India presents numerous options for businesses seeking to improve liquidity. The prominent ones are as follows:
Invoice Discounting
Invoice discounting provides suppliers early payment by selling their receivables at a discount to a financial institution, which then collects from the buyer on an invoice’s due date. The discount rate, based on the buyer’s creditworthiness, offers lower costs than traditional financing options. Invoice discounting provides suppliers with immediate liquidity while preserving their customer relationships.
Supplier Financing
Supplier financing (vendor financing) provides early invoice payment to suppliers via a financial institution, with buyer approval. Similar to invoice discounting, it involves collaboration between buyers, suppliers and financial institutions. This benefits suppliers lacking traditional credit access but having creditworthy buyer relationships, enabling sustained or scaled operations.
Reverse Factoring (or Buyer-Led Factoring)
In reverse factoring, the buyer initiates financing, contracting with a financial institution to pay suppliers early at a discount. The buyer then repays the financial institution at the agreed-upon payment terms. Reverse factoring allows buyers to extend payment terms and ensure prompt supplier payments. It is ideal for buyers with strong credit ratings looking to optimize their cash flow.
Dynamic Discounting
Dynamic discounting offers suppliers early payment in exchange for a variable discount, depending on how early the payment is made. The earlier the payment, the greater the discount. This allows suppliers liquidity flexibility and buyers cash flow management, benefiting both through quicker payments and adjustable discounts.
Inventory Financing
Inventory financing allows businesses to leverage their inventory as collateral for short-term loans. This proves beneficial for suppliers or buyers requiring working capital tied to their inventory. By using inventory as collateral, businesses can access funds for immediate cash flow needs or to support supply chain operations, avoiding expensive loans or credit and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Purchase Order Financing
Purchase order financing enables suppliers to secure funding based on confirmed purchase orders, not invoices, addressing capital needs for large orders. Using purchase orders as collateral, suppliers cover production or procurement costs. Financial institutions fund the supplier, and upon delivery, the buyer pays the financier, who then repays the loan. This arrangement allows suppliers to meet customer demand without significant upfront capital.
Supply Chain Finance Process – How It Works
Through technology-enabled collaboration between buyers, suppliers, and financial institutions, and the efficient handling of receivables and payables, supply chain finance in India optimizes cash flow and working capital. The process is as follows:
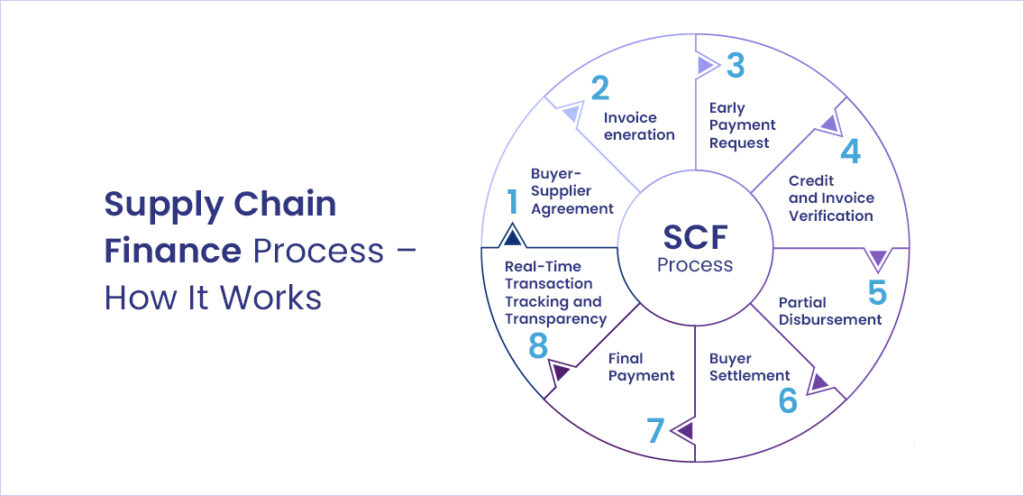
- Buyer-Supplier Agreement: The buyer (corporate) and the supplier (typically an MSME) agree on payment terms for goods or services. The buyer may extend the payment terms to manage cash flow, while the supplier accepts these terms knowing they get early payments.
- Invoice Generation: After delivery of agreed goods or services, the supplier issues invoices with specified due dates (30, 60, 90 days), opting for early payment.
- Early Payment Request: Supplier submits invoices to a financial institution, maybe via supply chain platforms, for automated early payment processing.
- Credit and Invoice Verification: The financial institution verifies invoices and assesses buyer’s creditworthiness. If the buyer is deemed financially stable, the institution approves the request for early payment and offers a discounted amount to the supplier.
- Partial Disbursement: Once approved, the financial institution disburses 90-95% of the invoice amount to the supplier, minus a discount.
- Buyer Settlement: Buyer pays the full invoice amount to the financial institution on the due date. This settles the debt and ensures the buyer maintains favourable payment terms.
- Final Payment: Once the buyer’s payment is received, the financial institution releases the remaining balance of the invoice (minus any applicable fees) to the supplier. This completes the transaction.
- Real-Time Transaction Tracking and Transparency: Throughout this exchange, the underlying Technology provides real-time transaction tracking, ensuring transparency and trust between buyer and supplier.
Conclusion
The deep mobile penetration and network connectivity across the length and breadth of the country is a key driving factor for supply chain finance in India. It has grown beyond just a mere transactional exchange, it’s now a strategic lever transforming India’s business ecosystem, particularly for MSMEs. By streamlining cash flow and leveraging collaborative relationships, supply chain finance empowers MSMEs to address market volatility and drive sustainable growth. With real-time transparency and technology-driven processes, it not only improves cash flow but also delivers stronger business relationships across the entire supply chain.
Given the evolving nature and the complexities involved in supply chain finance, a platform like Loan Frame’s marketplace becomes indispensable, connecting buyers, suppliers and financial institutions in a seamless, technology-driven ecosystem. Our platform helps suppliers access fast, affordable working capital, allows buyers to optimize their payment terms and opens new opportunities for financial institutions to grow their portfolios.
Whether you are a supplier in need of liquidity, a buyer looking to extend payment terms without disrupting relationships or a financial institution seeking to tap into a growing market, Loan Frame offers you the right solutions.
Book a demo today to explore how we can help your business thrive.